The 6 week postnatal check- that’s when you get the all clear and it’s back to business as usual, right?
That’s how I remember feeling anyway, and from my experience training new mums, I know I’m not alone.
I remember sitting there and asking, “So I’m ok to go back to exercise now?”
And I got lucky, because my GP said yes, but advised that giving birth means my body had been through some big changes, and 3 months would be better, to really have time to recover.
That, plus having a baby who didn’t sleep well, plus geting mastitis at 3 months postpartum, meant that I didn’t get back to training as quickly as I had planned. Which probably saved me from doing myself some harm.
Because although I’d been a personal trainer for 7 years, I didn’t have any postnatal qualifications at that point, and the general message I’d absorbed from the media is that if you’re in good shape you should ‘bounce back’.
And I was fit, so I should be fine. In fact, because I worked in the fitness industry I felt I should be seen to recover and get my fitness back quickly, and I was very fortunate to have a doctor who gave me some good advice (and to be too exhausted to argue with it)!
Because The 6 Week Postnatal Check Does Not Mean You’re Ready To Exercise!
However, this hinges upon what your definition of ‘exercise’ is. Because I could also say you don’t need to wait 6 weeks before you exercise.
The problem I come across is that many doctors aren’t specific about what they mean by exercise. So while they’re thinking a few walks and pelvic floor exercises would be good, I know a lot of women will be thinking ‘back to my old workout routine.”
What Happens If You Do Too Much Too Soon.
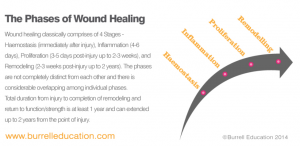
Even though you might feel ok at your 6 week check, it takes so much longer than we realise to recover from childbirth. Then there’s the pregnancy hormones, lack of sleep and breastfeeding to consider. I’ve written here about postnatal recovery already, and the potential consequences of too much exercise too soon, and this blog is a must-read example of what happened to one mum when she returned to exercise too quickly.
Your Pelvic Floor
The pelvic floor is the area that often pays the price if you overdo it, and unfortunately this is one of the things your doctor probably doesn’t tell you.
Pelvic Organ Prolapse is when 1 or more of your pelvic organs (bladder, rectum, uterus, intestines even) move out of place, and prolapse down into the wall of the vagina. I had 2 children, did my ante and post natal exercise qualification, and still hadn’t heard of this. (I’ve since studied both pregnancy and postnatal exercise to a higher level to rectify the gaps in the fitness industry’s basic training!)
And I really wish GPs, or even the hospital/ homebirth team, would give new mums some information on this AS STANDARD! Because prolapse can have such a huge impact on your life, I’m sure a little information would lead to a lot of mums making far more sensible decisions.
Diastasis Recti
This is something else that I really wish GPs would check, but generally they don’t. I can count on 1 hand the number of mums I’ve met (out of 100s) who have had their diastasis checked at their 6 week appointment. For more information about what exactly diastasis recti is, read this blog, but it’s another biggie in that if it isn’t healed, you’re at a higher risk of injury or pelvic floor problems if you do too much too soon.
 In fact, I don’t know about you, but my 6 week checks have been a quick blood pressure check and then asking what contraception I was using. In case the 6 week baby wasn’t enough!
In fact, I don’t know about you, but my 6 week checks have been a quick blood pressure check and then asking what contraception I was using. In case the 6 week baby wasn’t enough!
In many cases the check up is more about the baby than the mum, and even though one of mine was a seperate appointment than the baby check, it still didn’t go anywhere near as deep as it should. The only way to know for sure what’s happening with your pelvic floor is too see a Women’s Health Physio (if you’re local to me I recommend some here).
So What Can I Do?
I said before that you don’t have to wait for 6 weeks until you exercise, and you don’t. But I’m talking about exercise so gentle you may not even think of it as exercise.
You’re advised to start your pelvic floor exercises (kegels) as soon as you’ve had baby, and you can start doing some gentle deep core connection work after a few days. Even with a c-section, you can do these from around 7-14 days. I do this with clients and mums doing Restore My Core, as there can be a loss of responsiveness in those muscles, which needs to be restored.
Following on from this, progressing to glute exercises to promote pelvis and hip stability is also beneficial. This, plus some gentle walking when you feel up to it (and I’d advise a few weeks rather than a few days for that) can help in a number of ways:
Faster Recovery Post Birth
The pelvic floor exercises will increase circulation to the area, helping to heal any tears, and both the core and floor work will help your nervous system to re-connect to these muscles.
Healing Diastasis and Preventing Incontinence
The right exercises, especially those that involve the deep transversus abdominis and pelvic floor, will help to heal diastasis recti. And pelvic floor exercises will help you regain control if you’re suffering from any leaking post-birth.
Reduced Pain
Having a stronger core will help take the pressure off your back muscles, which have to pick up the slack when the rest of the core isn’t functioning properly. Some gentle stretching and release work can help with this too.
The best course of action is to follow a specific post natal restorative programme, such as Restore My Core, but to learn more now you can download my 10 Tips for getting into shape after baby. And remember- the most important thing in the early postnatal period is rest, and when you do start exercising it should make you feel better, not worse. If you feel fatigued after you may have over done it. Listen to your body, and take it slowly.